N,N-Di(2-hydroxyethyl)meta-chloroaniline (DHEA) is an organic compound that belongs to the class of anilines. It is a colorless liquid that is slightly soluble in water. DHEA is used as an intermediate in the production of dyes, pigments, and other chemicals. It can also be used as a corrosion inhibitor, a chelating agent, and a water softener. DHEA is also used as an intermediate for the production of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. It is a intermediate in the synthesis of Polyamides.
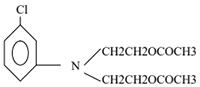
| TECHNICAL NAME | N, N DI (2-ACETOXY ETHYL) META CHLORO ANILINE |
|---|---|
| C.A.S. REGISTRY NUMBER | 26692-46-6 |
| EMPIRICAL FORMULA | C14 H18 Cl N O4 |
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT | 299.75 |
| PHYSICAL APPEARANCE | Dark Brown, Acetic Acid Solution. |
| PURITY | Perchloric Acid Titration: 50-60 % |
| USES | Coupling Agent For Disperse Dyes for Synthentic Fibres |
| TOXICITY | Corrosive, can Cause Burms when in Contact with Skin, Irritation to the Eyes, Harmful If Inhaled or Ingested. |
| PACKING | 220 KGS. H. D. P. E. Barrels. |
| SALES BASIS | 100 % Basis |